
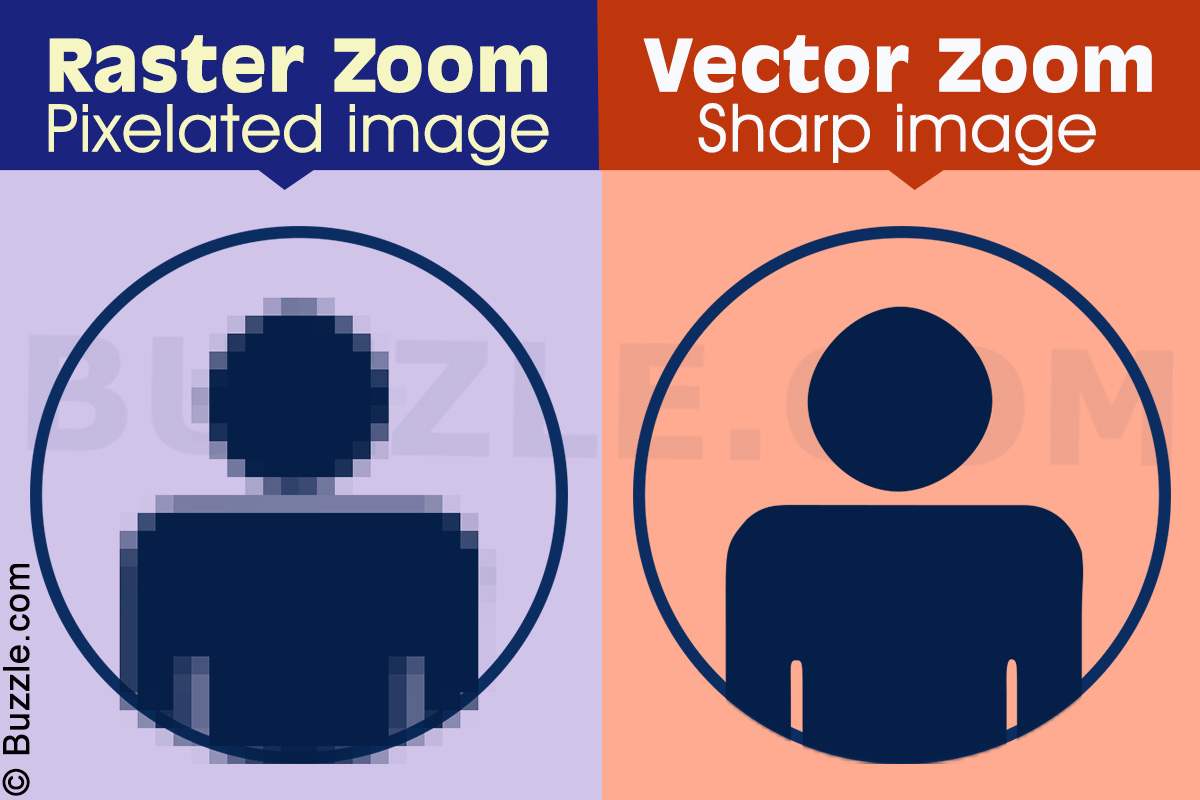
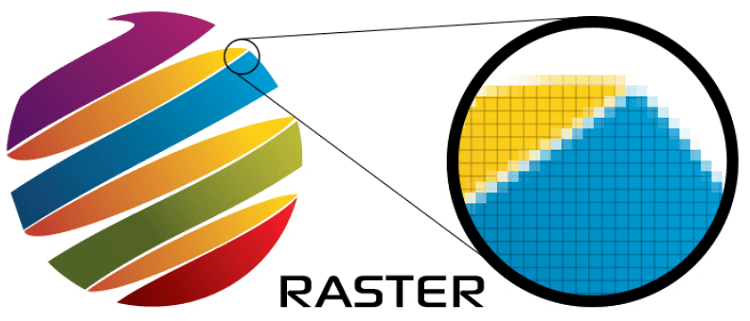
Vector graphics can save the day in such situations. What you don't want is for your client to ask for a much larger size and you sitting there stuck with a pixelated raster image. This makes them ideal for designs that need to be rendered in different sizes. The following images should help you understand the main differences between raster images and vector images.Īs you can see, there's no pixelation here because vectors aren't susceptible to this phenomenon. This is due to a process called pixelation, which you see when enlarging a raster image. The big difference is that vector graphics are scalable to any size without impacting the clarity. If raster images are made up of dots, bits, or pixels, vectors are made up of lines and curves. The simplest way to answer the question, "What is a Vector Image?" is to contrast it with another type of design element, which is the raster graphic or raster image. A vector is a geometric unit that has a magnitude as well as a direction, which leads to the term 'vector path.' These vector paths define how a line or curve is plotted on a display medium, usually a screen or monitor. In essence, they are plotted on a two-dimensional plane or even three-dimensional plane and are based on a mathematical concept called a vector.
The gist of these definitions points to the real meaning of vector graphics and vector images. Most of us have heard of vector graphics or vector images, but what is vector graphics in the context of design? According to Adobe's website, the vector graphics definition implies that these images have "points, lines, curves and shapes that are based on mathematical formulas." The technical vector image definition, according to Wikipedia, says that they are "computer graphics images that are defined in terms of points on a Cartesian plane, which are connected by lines and curves to form polygons and other shapes."


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
